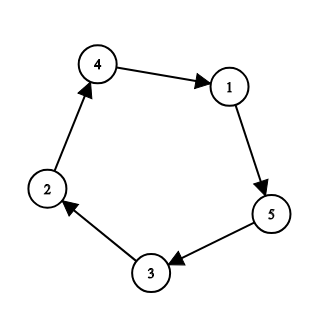
 Example: 5 kids in a circle, $p=[3,2,4,1,5]$ (or any cyclic shift). The information kids remembered is: $a_{1,1}=3,a_{1,2}=5,a_{2,1}=1,a_{2,2}=4;a_{3,1}=2,a_{3,2}=4,a_{4,1}=1,a_{4,2}=5,a_{5,1}=2,a_{5,2}=3$.
Example: 5 kids in a circle, $p=[3,2,4,1,5]$ (or any cyclic shift). The information kids remembered is: $a_{1,1}=3,a_{1,2}=5,a_{2,1}=1,a_{2,2}=4;a_{3,1}=2,a_{3,2}=4,a_{4,1}=1,a_{4,2}=5,a_{5,1}=2,a_{5,2}=3$.You have to restore the order of the kids in the circles using this information. If there are several answers, you may print any. It is guaranteed that at least one solution exists.
If you are Python programmer, consider using PyPy instead of Python when you submit your code.
Input
The first line of the input contains one integer $n(3\le n\le 2.10^5)$- the number of the kids.
The next $n$ lines contain $2$ integers each. The $i-th$ line contains two integers $a_{i,1}$ and $a_{i,2}(1\le a_{i,1},a_{i,2}\le n,a_{i,1}\ne a_{i,2})$- the kids the $i-th$ kid remembered, given in arbitrary order.
Output
Print $n$ integers $p_1,p_2,...,p_n$- permutation of integers from $1$ to $n$, which corresponds to the order of kids in the circle. If there are several answers, you may print any (for example, it doesn't matter which kid is the first in the circle). It is guaranteed that at least one solution exists.
Examples
input
Copy
5 3 5 1 4 2 4 1 5 2 3
output
Copy
3 2 4 1 5
input
Copy
3 2 3 3 1 1 2
output
Copy
3 1 2
#include <bits/stdc++.h> int main() { int n, i, j, k, u, v; scanf("%d", &n); std::vector<int> a(n + 1); for (i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { scanf("%d%d", &u, &v); if (u == n || v == n) j = u ^ v ^ n; a[u] ^= v; a[v] ^= u; } if (j == u || j == v) j ^= a[n]; for (i = n; n--; k = j, j = i, i = k ^ a[i]) printf("%d ", i); }
Không có nhận xét nào:
Đăng nhận xét